Page 117 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition May-Junel 2022
P. 117
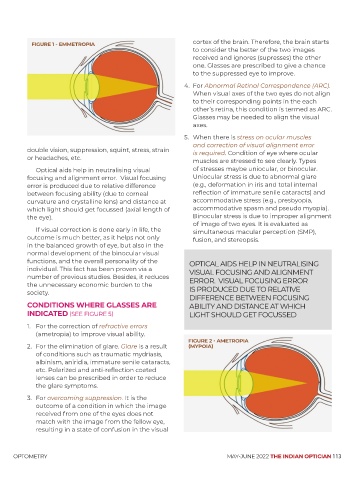
FIGURE 1 - EMMETROPIA cortex of the brain. Therefore, the brain starts
to consider the better of the two images
received and ignores (supresses) the other
one. Glasses are prescribed to give a chance
to the suppressed eye to improve.
4. For Abnormal Retinal Correspondence (ARC).
When visual axes of the two eyes do not align
to their corresponding points in the each
other’s retina, this condition is termed as ARC.
Glasses may be needed to align the visual
axes.
5. When there is stress on ocular muscles
and correction of visual alignment error
double vision, suppression, squint, stress, strain is required. Condition of eye where ocular
or headaches, etc. muscles are stressed to see clearly. Types
Optical aids help in neutralising visual of stresses maybe uniocular, or binocular.
focusing and alignment error. Visual focusing Uniocular stress is due to abnormal glare
error is produced due to relative difference (e.g., deformation in iris and total internal
between focusing ability (due to corneal reflection of immature senile cataracts) and
curvature and crystalline lens) and distance at accommodative stress (e.g., presbyopia,
which light should get focussed (axial length of accommodative spasm and pseudo myopia).
the eye). Binocular stress is due to improper alignment
of image of two eyes. It is evaluated as
If visual correction is done early in life, the simultaneous macular perception (SMP),
outcome is much better, as it helps not only fusion, and stereopsis.
in the balanced growth of eye, but also in the
normal development of the binocular visual
functions, and the overall personality of the OPTICAL AIDS HELP IN NEUTRALISING
individual. This fact has been proven via a VISUAL FOCUSING AND ALIGNMENT
number of previous studies. Besides, it reduces ERROR. VISUAL FOCUSING ERROR
the unnecessary economic burden to the
society. IS PRODUCED DUE TO RELATIVE
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FOCUSING
CONDITIONS WHERE GLASSES ARE ABILITY AND DISTANCE AT WHICH
INDICATED (SEE FIGURE 5) LIGHT SHOULD GET FOCUSSED
1. For the correction of refractive errors
(ametropia) to improve visual ability.
FIGURE 2 - AMETROPIA
2. For the elimination of glare. Glare is a result (MYPOIA)
of conditions such as traumatic mydriasis,
albinism, aniridia, immature senile cataracts,
etc. Polarized and anti-reflection coated
lenses can be prescribed in order to reduce
the glare symptoms.
3. For overcoming suppression. It is the
outcome of a condition in which the image
received from one of the eyes does not
match with the image from the fellow eye,
resulting in a state of confusion in the visual
OPTOMETRY MAY-JUNE 2022 THE INDIAN OPTICIAN 113