Page 105 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition May-Junel 2022
P. 105
iii) The sum of the lenses +1.75 / +0.50 x 45 and
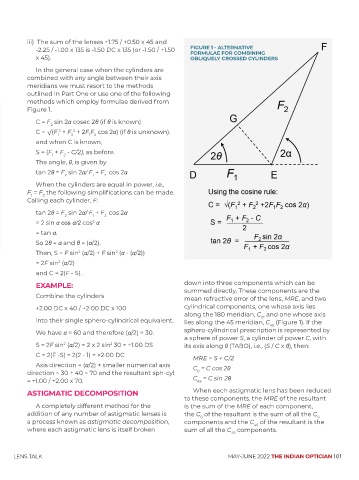
-2.25 / -1.00 x 135 is -1.50 DC x 135 (or -1.50 / +1.50 FIGURE 1 - ALTERNATIVE
FORMULAE FOR COMBINING
x 45). OBLIQUELY CROSSED CYLINDERS
In the general case when the cylinders are
combined with any angle between their axis
meridians we must resort to the methods
outlined in Part One or use one of the following
methods which employ formulae derived from
Figure 1.
C = F sin 2α cosec 2θ (if θ is known)
2
C = √(F + F + 2F F cos 2α) (if θ is unknown).
2
2
2
1
1
2
and when C is known,
S = (F + F - C/2), as before.
1 2
The angle, θ, is given by
tan 2θ = F sin 2α/ F + F cos 2α
1
2
2
When the cylinders are equal in power, i.e.,
F = F the following simplifications can be made.
2
1
Calling each cylinder, F:
tan 2θ = F sin 2α/ F + F cos 2α
2 1 2
= 2 sin α cos α/2 cos α
2
= tan α.
So 2θ = α and θ = (α/2).
Then, S = F sin (α/2) + F sin (α - (α/2))
2
2
= 2F sin (α/2)
2
and C = 2(F - S).
EXAMPLE: down into three components which can be
Combine the cylinders summed directly. These components are the
mean refractive error of the lens, MRE, and two
+2.00 DC x 40 / +2·00 DC x 100 cylindrical components, one whose axis lies
along the 180 meridian, C , and one whose axis
0
into their single sphero-cylindrical equivalent. lies along the 45 meridian, C (Figure 1). If the
45
We have α = 60 and therefore (α/2) = 30. sphero-cylindrical prescription is represented by
a sphere of power S, a cylinder of power C, with
S = 2F sin (α/2) = 2 x 2 sin 30 = +1.00 DS its axis along θ (TABO), i.e., (S / C x θ), then:
2
2
C = 2(F -S) = 2(2 - 1) = +2·00 DC MRE = S + C/2
Axis direction = (α/2) + smaller numerical axis C = C cos 2θ
direction = 30 + 40 = 70 and the resultant sph-cyl 0
= +1.00 / +2.00 x 70. C = C sin 2θ
45
ASTIGMATIC DECOMPOSITION When each astigmatic lens has been reduced
to these components, the MRE of the resultant
A completely different method for the is the sum of the MRE of each component,
addition of any number of astigmatic lenses is the C of the resultant is the sum of all the C
0
0
a process known as astigmatic decomposition, components and the C of the resultant is the
45
where each astigmatic lens is itself broken sum of all the C components.
45
LENS TALK MAY-JUNE 2022 THE INDIAN OPTICIAN 101