Page 121 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition September-October 2021
P. 121
Peripheral iridotomy is very effective for lowering
the IOP and opening the angles, although in
severe cases, more treatments are required, like
topical medications or filtration surgery.
Laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI) is a hand-
picked procedure for treating angle-closure
glaucoma that is caused due to relative or
absolute pupillary block. LPI removes the
pupillary block by allowing the aqueous to
pass straight from the posterior chamber
into the anterior chamber, bypassing the
pupil. An LPI is performed with an argon
medications and controlled effects. Medication laser, with neodymium: yttrium-aluminium-
choice is additionally influenced by the cost, garnet (Nd: YAG) laser. It's commonly used to
adverse effects, and dosing schedules. When treat an outsized range of clinical conditions,
medical treatment doesn't achieve adequate encompassing primary angle‐closure glaucoma,
pressure reduction with acceptable adverse primary angle-closure (narrow angles and no
effects, laser or incisional surgeries are indicated. signs of glaucomatous optic neuropathy). It
However, topical medications can cause adverse also includes patients that are primary angle-
effects such as dry eye, burning/stinging, itching, closure suspects (PACS) (patients with reversible
irritation, tearing, foreign body sensation, red- obstruction) and even eyes with secondary
eye, and blurred vision. Other systemic-related causes of iridocorneal angle-closure. Unaffected
adverse reactions are headache, vertigo, malaise, fellow eyes of patients who had angle closure
asthma symptoms, and Stevens-Johnson may have a 50% risk of developing angle-closure
syndrome. As glaucoma therapy requires long- glaucoma if not treated with prophylactic
term treatment, the adverse effects gradually iridotomy.
increase with the time of treatment. At the
end of the phase, the doctor recommends the In our study, the efficacy of laser peripheral
discontinuation of drops. iridotomy is observed as the treatment for
angle-closure glaucoma and as a prophylactic
Glaucoma can affect a patient’s quality of life measure for primary angle closure and primary
and impair their performance in a broad array of angle-closure suspects in terms of reducing
activities of daily living such as reading, walking intraocular pressure.
and driving. The quality of life is adversely
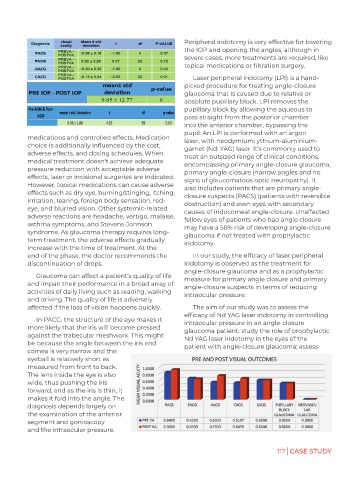
affected if the loss of vision happens quickly. The aim of our study was to assess the
efficacy of Nd YAG laser iridotomy in controlling
In PACG, the structure of the eye makes it intraocular pressure in an angle-closure
more likely that the iris will become pressed glaucoma patient; study the role of prophylactic
against the trabecular meshwork. This might Nd YAG laser iridotomy in the eyes of the
be because the angle between the iris and patient with angle-closure glaucoma; assess
cornea is very narrow and the
eyeball is relatively short as
measured from front to back.
The lens inside the eye is also
wide, thus pushing the iris
forward, and as the iris is thin, it
makes it fold into the angle. The
diagnosis depends largely on
the examination of the anterior
segment and gonioscopy
and the intraocular pressure.
117 | CASE STUDY