Page 116 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition November-December 2021
P. 116
field testing can also be helpful in the diagnosis
of NAION. NAION often presents with an inferior
altitudinal, inferior nasal, or cecocentral visual
field defect (Figure 4). In rare cases, the visual
4
field defect may present as a pure central
defect. Surprisingly, colour vision is typically
6
unaffected due to relatively untouched macular
fibers of the nerve in this condition. 6
MANAGEMENT
Unilateral disc edema may also be a sign
of a variety of other disorders including optic
disc drusen, asymmetric papilledema, optic
neuritis, and arteritic anterior ischemic optic
neuropathy (AAION). Optic disc drusen is
5
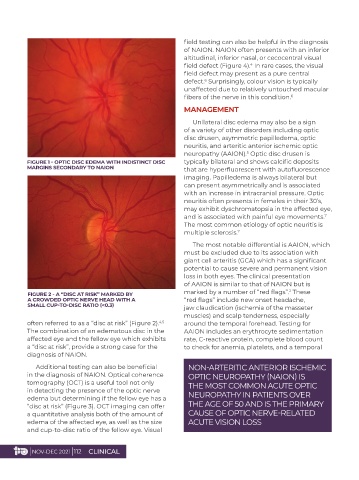
FIGURE 1 - OPTIC DISC EDEMA WITH INDISTINCT DISC typically bilateral and shows calcific deposits
MARGINS SECONDARY TO NAION that are hyperfluorescent with autofluorescence
imaging. Papilledema is always bilateral but
can present asymmetrically and is associated
with an increase in intracranial pressure. Optic
neuritis often presents in females in their 30’s,
may exhibit dyschromatopsia in the affected eye,
and is associated with painful eye movements.
7
The most common etiology of optic neuritis is
multiple sclerosis. 7
The most notable differential is AAION, which
must be excluded due to its association with
giant cell arteritis (GCA) which has a significant
potential to cause severe and permanent vision
loss in both eyes. The clinical presentation
of AAION is similar to that of NAION but is
2
FIGURE 2 - A “DISC AT RISK” MARKED BY marked by a number of “red flags”. These
A CROWDED OPTIC NERVE HEAD WITH A “red flags” include new onset headache,
SMALL CUP-TO-DISC RATIO (<0.3) jaw claudication (ischemia of the masseter
muscles) and scalp tenderness, especially
often referred to as a “disc at risk” (Figure 2). around the temporal forehead. Testing for
4,5
The combination of an edematous disc in the AAION includes an erythrocyte sedimentation
affected eye and the fellow eye which exhibits rate, C-reactive protein, complete blood count
a “disc at risk”, provide a strong case for the to check for anemia, platelets, and a temporal
diagnosis of NAION.
Additional testing can also be beneficial NON-ARTERITIC ANTERIOR ISCHEMIC
in the diagnosis of NAION. Optical coherence OPTIC NEUROPATHY (NAION) IS
tomography (OCT) is a useful tool not only THE MOST COMMON ACUTE OPTIC
in detecting the presence of the optic nerve NEUROPATHY IN PATIENTS OVER
edema but determining if the fellow eye has a
“disc at risk” (Figure 3). OCT imaging can offer THE AGE OF 50 AND IS THE PRIMARY
a quantitative analysis both of the amount of CAUSE OF OPTIC NERVE-RELATED
edema of the affected eye, as well as the size ACUTE VISION LOSS
and cup-to-disc ratio of the fellow eye. Visual
| NOV-DEC 2021 | 112 CLINICAL