Page 106 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition November-December 2021
P. 106
A +4.00 D lens which has been designed to be point focal for out to 30º from the optical axis.
a working distance of one-third metre, typical of that used for Beyond this, almost at the edge
near vision, would require a base curve of +7.50 D. The off-axis of the field of fixation, there is
performance of this design is shown in Figure 3(a) where it can a small amount of astigmatism
be seen that the lens is point focal out to 40º but suffers a power with the mean oblique error
error of +0.30 D for this zone of the lens. Figure 3(b) shows that if reaching about -0.75 D at 40º.
this form is used for distance vision, the oblique astigmatic error When this design with a
reaches almost +0.40 D but the mean oblique error is now zero. +6.25 D base curve is used
When aspherical surfaces are employed, there is another for near vision, however, the
way of optimising the distance vision forms for near vision . Use aberrations become more
6
of an aspherical surface removes the restriction of Tscherning’s severe. At 35º there is -0.60 D
Ellipse in that a best form lens can be made with any base curve of both astigmatism and mean
providing the eccentricity of the surface is correctly chosen to oblique error which increases
neutralise the aberrational astigmatism arising from oblique to over -1.00 D at 40º.
refraction. to be continued...
Thus, a +4.00 D lens made with a +6.25 D spherical front
surface would become point focal for distance vision by the use
of a concave aspherical surface shaped like an oblate ellipsoid
(a surface similar to that of a rugby ball standing on one end).
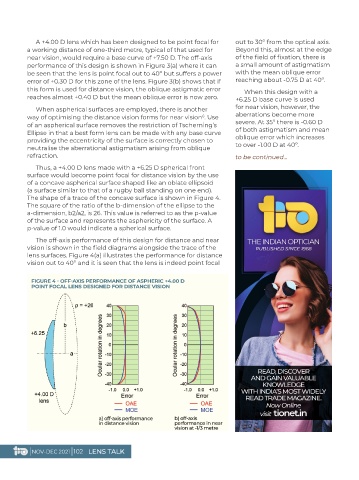
The shape of a trace of the concave surface is shown in Figure 4.
The square of the ratio of the b-dimension of the ellipse to the
a-dimension, b2/a2, is 26. This value is referred to as the p-value
of the surface and represents the asphericity of the surface. A
p-value of 1.0 would indicate a spherical surface.
The off-axis performance of this design for distance and near
vision is shown in the field diagrams alongside the trace of the
lens surfaces. Figure 4(a) illustrates the performance for distance
vision out to 40º and it is seen that the lens is indeed point focal
FIGURE 4 - OFF-AXIS PERFORMANCE OF ASPHERIC +4.00 D
POINT FOCAL LENS DESIGNED FOR DISTANCE VISION
| NOV-DEC 2021 | 102 LENS TALK