Page 127 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition March-April 2021
P. 127
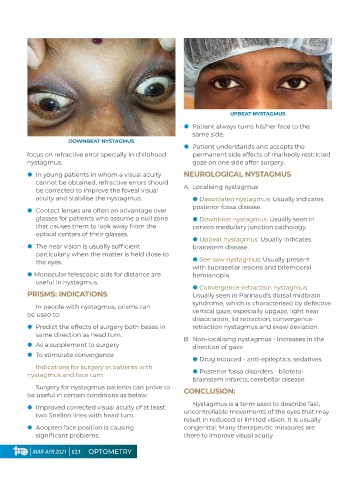
UPBEAT NYSTAGMUS
z Patient always turns his/her face to the
same side.
DOWNBEAT NYSTAGMUS
z Patient understands and accepts the
focus on refractive error specially in childhood permanent side effects of markedly restricted
nystagmus. gaze on one side after surgery.
z In young patients in whom a visual acuity NEUROLOGICAL NYSTAGMUS
cannot be obtained, refractive errors should
be corrected to improve the foveal visual A. Localising nystagmus
acuity and stabilise the nystagmus. z Dissociated nystagmus: Usually indicates
posterior fossa disease.
z Contact lenses are often an advantage over
glasses for patients who assume a null zone z Downbeat nystagmus: Usually seen in
that causes them to look away from the cervico medullary junction pathology.
optical centers of their glasses.
z Upbeat nystagmus: Usually indicates
z The near vision is usually sufficient brainstem disease.
particularly when the matter is held close to
z See-saw nystagmus: Usually present
the eyes.
with suprasellar lesions and bitemporal
z Monocular telescopic aids for distance are hemianopia.
useful in nystagmus.
z Convergence-retraction nystagmus:
PRISMS: INDICATIONS Usually seen in Parinaud’s dorsal midbrain
syndrome, which is characterised by defective
In people with nystagmus, prisms can
be used to: vertical gaze, especially upgaze, light near
dissociation, lid retraction, convergence-
z Predict the effects of surgery both bases in retraction nystagmus and skew deviation.
same direction as head turn.
B. Non-localising nystagmus - Increases in the
z As a supplement to surgery direction of gaze
z To stimulate convergence
z Drug induced - anti-epileptics, sedatives
Indications for surgery in patients with
z Posterior fossa disorders - bilateral
nystagmus and face turn
brainstem infarcts, cerebellar disease.
Surgery for nystagmus patients can prove to
CONCLUSION:
be useful in certain conditions as below:
Nystagmus is a term used to describe fast,
z Improved corrected visual acuity of at least
two Snellen lines with head turn. uncontrollable movements of the eyes that may
result in reduced or limited vision. It is usually
z Adopted face position is causing congenital. Many therapeutic measures are
significant problems. there to improve visual acuity.
| MAR-APR 2021 | 123 OPTOMETRY
Mar-Apr 2021 SK.indd 71 26-04-2021 14:01