Page 112 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition September-October 2021
P. 112
originate from alternative sites. A calcium
embolus typically appears as large, white and
globular, and commonly is impacted into the
proximal retinal artery branches (Figure 3).
Calcium emboli commonly originate from a
heart valve. Platelet fibrin aggregates present
as elongated dull grey opacities. Platelet-fibrin
aggregates are dull grey-white, are often difficult
to observe, and typically arise from atheromas
in the carotid arteries (Figure 4). A fat embolus
8
can occur when a fractured long bone releases
droplets of fat into the bloodstream. These
commonly travel to the lungs or brain, resulting
in pulmonary emboli or stroke. Foreign body
9
emboli, such as talc, can deposit in the retinal
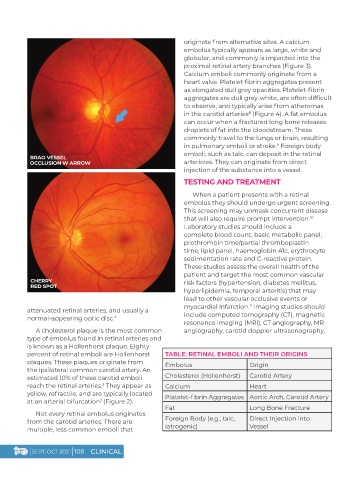
BRAO VESSEL
OCCLUSION W ARROW arterioles. They can originate from direct
injection of the substance into a vessel.
TESTING AND TREATMENT
When a patient presents with a retinal
embolus they should undergo urgent screening.
This screening may unmask concurrent disease
that will also require prompt intervention.
10
Laboratory studies should include a
complete blood count, basic metabolic panel,
prothrombin time/partial thromboplastin
time, lipid panel, haemoglobin A1c, erythrocyte
sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein.
These studies assess the overall health of the
patient and target the most common vascular
CHERRY risk factors (hypertension, diabetes mellitus,
RED SPOT
hyperlipidemia, temporal arteritis) that may
lead to other vascular occlusive events or
myocardial infarction. Imaging studies should
11
attenuated retinal arteries, and usually a
normal-appearing optic disc. include computed tomography (CT), magnetic
7
resonance imaging (MRI), CT angiography, MR
A cholesterol plaque is the most common angiography, carotid doppler ultrasonography,
type of embolus found in retinal arteries and
is known as a Hollenhorst plaque. Eighty
percent of retinal emboli are Hollenhorst TABLE: RETINAL EMBOLI AND THEIR ORIGINS
plaques. These plaques originate from Embolus Origin
the ipsilateral common carotid artery. An
estimated 10% of these carotid emboli Cholesterol (Hollenhorst) Carotid Artery
reach the retinal arteries. They appear as Calcium Heart
3
yellow, refractile, and are typically located Platelet-fibrin Aggregates Aortic Arch, Carotid Artery
at an arterial bifurcation (Figure 2).
2
Fat Long Bone Fracture
Not every retinal embolus originates
from the carotid arteries. There are Foreign Body (e.g., talc, Direct Injection into
multiple, less common emboli that iatrogenic) Vessel
| SEPT-OCT 2021 | 108 CLINICAL