Page 89 - The Indian Digital Edition September-October 2020
P. 89
may also have neuro-muscular
symptoms, including peripheral
neuropathy, multiple sclerosis or
spastic paraplegia among others. Only
about 20% of cases have systemic
manifestations with extreme variation
in severity .
(5)
Ocular characteristics of DOA
include reduced visual acuity, visual
field scotomas, colour vision defects
and rarely progressive external
ophthalmoplegias. There is a rare
variation of DOA that results from
mutation of the OPA3 gene that
results in optic atrophy and cataract
formation . In the OPA3 variation,
(1)
there is early optic atrophy followed
by later formation of cortical lens
changes. These signs occur in the
absence of systemic manifestations .
(5)
The classic clinical sign of OPA1
type DOA is bilateral, symmetric
optic nerve pallor that is usually
most obvious on the temporal side
of the optic disc (Figures 1a and 1b) .
(3)
Excavation of the disc may or may
not be present. Vision loss is highly
variable even within the same family
and typically ranges from 6/6 (20/20)
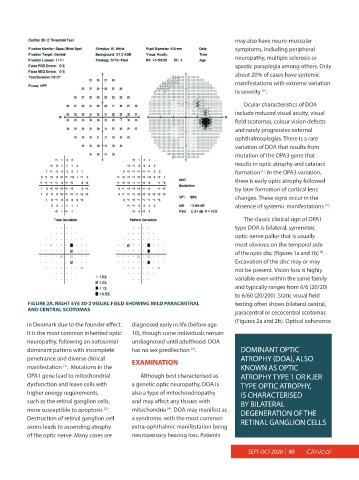
to 6/60 (20/200). Static visual field
FIGURE 2A. RIGHT EYE 30-2 VISUAL FIELD SHOWING MILD PARACENTRAL testing often shows bilateral central,
AND CENTRAL SCOTOMAS paracentral or cecocentral scotomas
(Figures 2a and 2b). Optical coherence
in Denmark due to the founder effect. diagnosed early in life (before age
It is the most common inherited optic 10), though some individuals remain
neuropathy, following an autosomal undiagnosed until adulthood. DOA
dominant pattern with incomplete has no sex predilection . DOMINANT OPTIC
(3)
penetrance and diverse clinical EXAMINATION ATROPHY (DOA), ALSO
manifestation . Mutations in the KNOWN AS OPTIC
(1)
OPA1 gene lead to mitochondrial Although best characterised as ATROPHY TYPE 1 OR KJER
dysfunction and leave cells with a genetic optic neuropathy, DOA is TYPE OPTIC ATROPHY,
higher energy requirements, also a type of mitochondriopathy IS CHARACTERISED
such as the retinal ganglion cells, and may affect any tissues with BY BILATERAL
more susceptible to apoptosis . mitochondria . DOA may manifest as DEGENERATION OF THE
(4)
(2)
Destruction of retinal ganglion cell a syndrome, with the most common RETINAL GANGLION CELLS
axons leads to ascending atrophy extra-ophthalmic manifestation being
of the optic nerve. Many cases are neurosensory hearing loss. Patients
SEPT-OCT 2020 | 85 Clinical