Page 142 - July-August 2020
P. 142
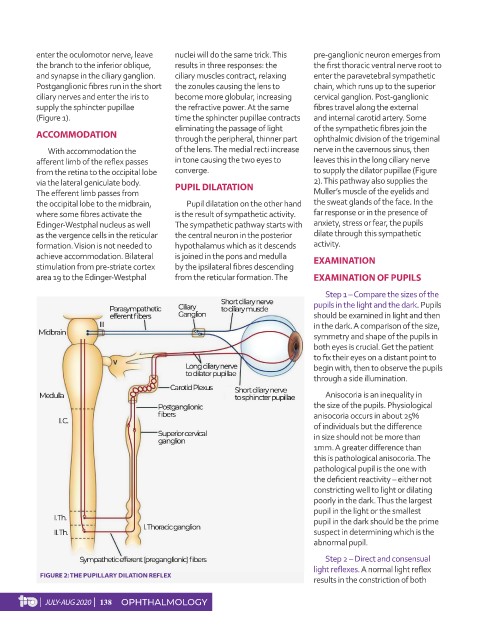
enter the oculomotor nerve, leave nuclei will do the same trick. This pre-ganglionic neuron emerges from
the branch to the inferior oblique, results in three responses: the the first thoracic ventral nerve root to
and synapse in the ciliary ganglion. ciliary muscles contract, relaxing enter the paravetebral sympathetic
Postganglionic fibres run in the short the zonules causing the lens to chain, which runs up to the superior
ciliary nerves and enter the iris to become more globular, increasing cervical ganglion. Post-ganglionic
supply the sphincter pupillae the refractive power. At the same fibres travel along the external
(Figure 1). time the sphincter pupillae contracts and internal carotid artery. Some
eliminating the passage of light of the sympathetic fibres join the
ACCOMMODATION through the peripheral, thinner part ophthalmic division of the trigeminal
With accommodation the of the lens. The medial recti increase nerve in the cavernous sinus, then
afferent limb of the reflex passes in tone causing the two eyes to leaves this in the long ciliary nerve
from the retina to the occipital lobe converge. to supply the dilator pupillae (Figure
via the lateral geniculate body. PUPIL DILATATION 2). This pathway also supplies the
The efferent limb passes from Muller’s muscle of the eyelids and
the occipital lobe to the midbrain, Pupil dilatation on the other hand the sweat glands of the face. In the
where some fibres activate the is the result of sympathetic activity. far response or in the presence of
Edinger-Westphal nucleus as well The sympathetic pathway starts with anxiety, stress or fear, the pupils
as the vergence cells in the reticular the central neuron in the posterior dilate through this sympathetic
formation. Vision is not needed to hypothalamus which as it descends activity.
achieve accommodation. Bilateral is joined in the pons and medulla EXAMINATION
stimulation from pre-striate cortex by the ipsilateral fibres descending
area 19 to the Edinger-Westphal from the reticular formation. The EXAMINATION OF PUPILS
Step 1 – Compare the sizes of the
pupils in the light and the dark. Pupils
should be examined in light and then
in the dark. A comparison of the size,
symmetry and shape of the pupils in
both eyes is crucial. Get the patient
to fix their eyes on a distant point to
begin with, then to observe the pupils
through a side illumination.
Anisocoria is an inequality in
the size of the pupils. Physiological
anisocoria occurs in about 25%
of individuals but the difference
in size should not be more than
1mm. A greater difference than
this is pathological anisocoria. The
pathological pupil is the one with
the deficient reactivity – either not
constricting well to light or dilating
poorly in the dark. Thus the largest
pupil in the light or the smallest
pupil in the dark should be the prime
suspect in determining which is the
abnormal pupil.
Step 2 – Direct and consensual
light reflexes. A normal light reflex
FIGURE 2: THE PUPILLARY DILATION REFLEX
results in the constriction of both
| JULY-AUG 2020 | 138 OPHTHALMOLOGY