Page 167 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition Jan-Feb 2020
P. 167
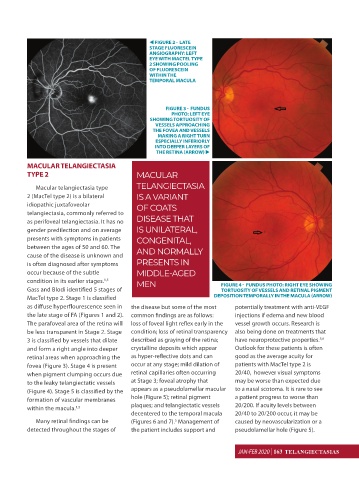
FIGURE 2 - LATE
STAGE FLUORESCEIN
ANGIOGRAPHY: LEFT
EYE WITH MACTEL TYPE
2 SHOWING POOLING
OF FLUORESCEIN
WITHIN THE
TEMPORAL MACULA
FIGURE 3 - FUNDUS
PHOTO: LEFT EYE
SHOWING TORTUOSITY OF
VESSELS APPROACHING
THE FOVEA AND VESSELS
MAKING A RIGHT TURN
ESPECIALLY INFERIORLY
INTO DEEPER LAYERS OF
THE RETINA (ARROW)
MACULAR TELANGIECTASIA
TYPE 2 MACULAR
Macular telangiectasia type TELANGIECTASIA
2 (MacTel type 2) is a bilateral IS A VARIANT
idiopathic juxtafoveolar OF COATS
telangiectasia, commonly referred to
as perifoveal telangiectasia. It has no DISEASE THAT
gender predilection and on average IS UNILATERAL,
presents with symptoms in patients CONGENITAL,
between the ages of 50 and 60. The AND NORMALLY
cause of the disease is unknown and
is often diagnosed after symptoms PRESENTS IN
occur because of the subtle MIDDLE-AGED
condition in its earlier stages. MEN FIGURE 4 - FUNDUS PHOTO: RIGHT EYE SHOWING
1,5
Gass and Blodi identified 5 stages of TORTUOSITY OF VESSELS AND RETINAL PIGMENT
MacTel type 2. Stage 1 is classified DEPOSITION TEMPORALLY IN THE MACULA (ARROW)
as diffuse hyperflourescence seen in the disease but some of the most potentially treatment with anti-VEGF
the late stage of FA (Figures 1 and 2). common findings are as follows: injections if edema and new blood
The parafoveal area of the retina will loss of foveal light reflex early in the vessel growth occurs. Research is
be less transparent in Stage 2. Stage condition; loss of retinal transparency also being done on treatments that
5,6
3 is classified by vessels that dilate described as graying of the retina; have neuroprotective properties.
and form a right angle into deeper crystalline deposits which appear Outlook for these patients is often
retinal areas when approaching the as hyper-reflective dots and can good as the average acuity for
fovea (Figure 3). Stage 4 is present occur at any stage; mild dilation of patients with MacTel type 2 is
when pigment clumping occurs due retinal capillaries often occurring 20/40, however visual symptoms
to the leaky telangiectatic vessels at Stage 3; foveal atrophy that may be worse than expected due
(Figure 4). Stage 5 is classified by the appears as a pseudolamellar macular to a nasal scotoma. It is rare to see
formation of vascular membranes hole (Figure 5); retinal pigment a patient progress to worse than
within the macula. plaques; and telangiectatic vessels 20/200. If acuity levels between
1,5
decentered to the temporal macula 20/40 to 20/200 occur, it may be
Many retinal findings can be (Figures 6 and 7). Management of caused by neovascularization or a
5
detected throughout the stages of the patient includes support and pseudolamellar hole (Figure 5).
JAN-FEB 2020 | 163 TELANGIECTASIAS
January-February 2020 SK.indd 76 02/15/2020 16:09