Page 102 - The Indian Digital Edition September-October 2020
P. 102
target and to maintain this fixation visual sensory stimulus. than a typical eye exam. Ideally, a
while the athlete and/or the object is Focus Flexibility: The ability to visual performance evaluation should
in motion or stationary. These visual be performed by an eye doctor
skills make up the two eye movement change focus from a faraway object to who specialises in this area. There
systems used i.e. Smooth Pursuit a near one or vice versa. are a number of tests that a sports
Tracking and Fast Saccadic Tracking. Visual Concentration: Ability to vision eye optometrist along with
focus your attention on the athletic ophthalmologists, athletic trainers, and
Central and Peripheral
Awareness: Ability of an athlete to task while filtering out peripheral coaches, can conduct to help identify
distraction. Poor visual concentration
maintain central fixation on a target and address your visual strengths and
10
yet to be aware of what is happening may result in an overall poor motor weaknesses.
response and also result in responses
to the sides or in the peripheral WHY DO WE NEED SPORTS
visual field. Several sports require not only being late but also inaccurate. VISION SCREENINGS?
high degrees of central-peripheral Colour Vision: The ability to
awareness – typical situations are distinguish different colours clearly Statistics taken from sports vision
where athletes must concentrate on a and accurately. Deficits in colour vision screenings at the Olympic and junior
ball (central fixation) while also being can cause you to incorrectly react to a Olympic level shows the visual status
aware of the position of teammates, visual stimulus because you are unable of different sports persons –20%
opponents and boundary lines. to distinguish the object/person from of athletes competing at a high
the “background noise.” level tournament have never had
Eye Hand/Feet/Body a complete eye examination. 30%
Coordination: This skill involves the VISUAL SKILLS EVALUATION had less than 20/20 vision. 25% had
integration of the eyes and the hands/ decreased depth perception. 26%
body. It determines the effectiveness Visual performance evaluation, is had poor eye-hand coordination for
of a perceptual motor response to a quite different and more extensive the demand of their sport. 12% had
inaccurate eye movement abilities
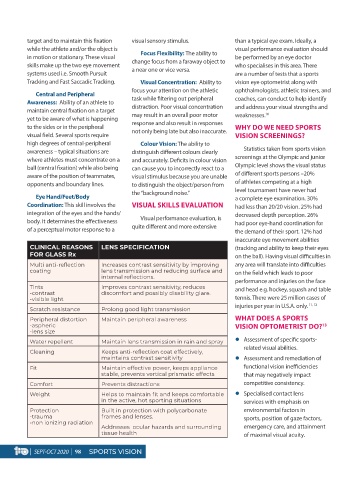
CLINICAL REASONS LENS SPECIFICATION (tracking and ability to keep their eyes
FOR GLASS Rx on the ball). Having visual difficulties in
Multi anti-reflection Increases contrast sensitivity by improving any area will translate into difficulties
coating lens transmission and reducing surface and on the field which leads to poor
internal reflections.
performance and injuries on the face
Tints Improves contrast sensitivity, reduces and head e.g. hockey, squash and table
-contrast discomfort and possibly disability glare.
-visible light tennis. There were 25 million cases of
injuries per year in U.S.A. only. 11, 12
Scratch resistance Prolong good light transmission
Peripheral distortion Maintain peripheral awareness WHAT DOES A SPORTS
-aspheric VISION OPTOMETRIST DO? 13
-lens size
Water repellent Maintain lens transmission in rain and spray Assessment of specific sports-
related visual abilities.
Cleaning Keeps anti-reflection coat effectively,
maintains contrast sensitivity Assessment and remediation of
Fit Maintain effective power, keeps appliance functional vision inefficiencies
stable, prevents vertical prismatic effects that may negatively impact
Comfort Prevents distractions competitive consistency.
Weight Helps to maintain fit and keeps comfortable Specialised contact lens
in the active, hot sporting situations services with emphasis on
Protection Built in protection with polycarbonate environmental factors in
-trauma frames and lenses. sports, position of gaze factors,
-non ionizing radiation
Addresses ocular hazards and surrounding emergency care, and attainment
tissue health of maximal visual acuity.
| SEPT-OCT 2020 | 98 SPORTS VISION