Page 133 - July-August 2020
P. 133
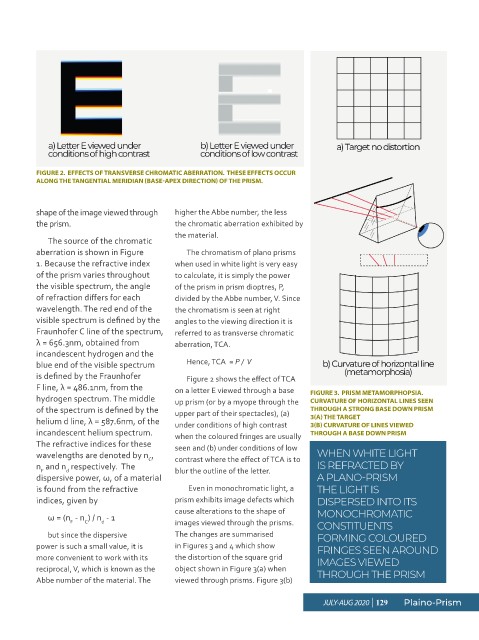
FIGURE 2. EFFECTS OF TRANSVERSE CHROMATIC ABERRATION. THESE EFFECTS OCCUR
ALONG THE TANGENTIAL MERIDIAN (BASE-APEX DIRECTION) OF THE PRISM.
shape of the image viewed through higher the Abbe number, the less
the prism. the chromatic aberration exhibited by
the material.
The source of the chromatic
aberration is shown in Figure The chromatism of plano prisms
1. Because the refractive index when used in white light is very easy
of the prism varies throughout to calculate, it is simply the power
the visible spectrum, the angle of the prism in prism dioptres, P,
of refraction differs for each divided by the Abbe number, V. Since
wavelength. The red end of the the chromatism is seen at right
visible spectrum is defined by the angles to the viewing direction it is
Fraunhofer C line of the spectrum, referred to as transverse chromatic
λ = 656.3nm, obtained from aberration, TCA.
incandescent hydrogen and the
blue end of the visible spectrum Hence, TCA = P / V
is defined by the Fraunhofer Figure 2 shows the effect of TCA
F line, λ = 486.1nm, from the on a letter E viewed through a base FIGURE 3. PRISM METAMORPHOPSIA.
hydrogen spectrum. The middle up prism (or by a myope through the CURVATURE OF HORIZONTAL LINES SEEN
of the spectrum is defined by the upper part of their spectacles), (a) THROUGH A STRONG BASE DOWN PRISM
helium d line, λ = 587.6nm, of the under conditions of high contrast 3(A) THE TARGET
3(B) CURVATURE OF LINES VIEWED
incandescent helium spectrum. when the coloured fringes are usually THROUGH A BASE DOWN PRISM
The refractive indices for these seen and (b) under conditions of low
wavelengths are denoted by n , contrast where the effect of TCA is to WHEN WHITE LIGHT
C
n and n respectively. The blur the outline of the letter. IS REFRACTED BY
d
F
dispersive power, ω, of a material A PLANO-PRISM
is found from the refractive Even in monochromatic light, a THE LIGHT IS
indices, given by prism exhibits image defects which DISPERSED INTO ITS
cause alterations to the shape of MONOCHROMATIC
ω = (n - n ) / n - 1
F C d images viewed through the prisms. CONSTITUENTS
but since the dispersive The changes are summarised FORMING COLOURED
power is such a small value, it is in Figures 3 and 4 which show FRINGES SEEN AROUND
more convenient to work with its the distortion of the square grid IMAGES VIEWED
reciprocal, V, which is known as the object shown in Figure 3(a) when THROUGH THE PRISM
Abbe number of the material. The viewed through prisms. Figure 3(b)
JULY-AUG 2020 | 129 Plaino-Prism